IoT Routes Architecture
➡ Role-based deployment model
The IoTRoutes platform is based on a modular, role-based architecture, allowing deployment to be adapted according to operational needs and infrastructure size.
This model, described as a “Role-Based Modular Monolith” combines the simplicity of a monolith with the flexibility of a microservices deployment. Each component of the system can be enabled or disabled depending on the server’s role in the deployment.
Operating principles
Modular deployment by role:
The administrator can assign specific roles to each server or instance as needed:Workers : servers dedicated to data processing, acquisition and management of message queues.
Messaging / MQTT Brokers : servers reserved for real-time communication with connected devices.
Web Access / Web Client : servers dedicated to user access via the web interface or REST APIs.
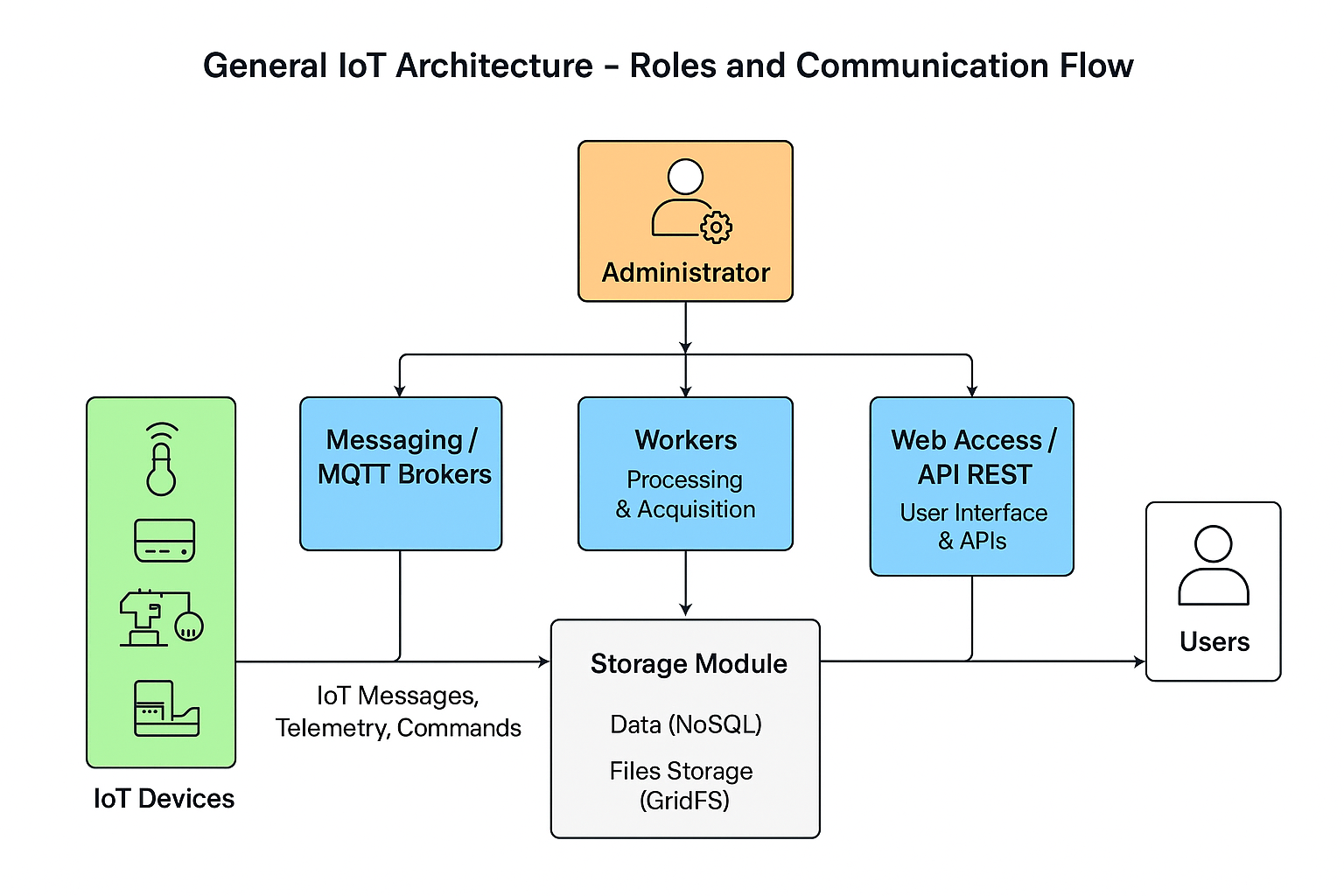
Deployment flexibility:
This approach allows both distributed deployment (several specialized servers per role) and standalone mode on a single instance, ideal for test or demonstration environments (sandbox).Simplicity and scalability: :
This model allows roles to be added or reassigned quickly without complex maintenance or requiring extensive microservice orchestration.
The system thus maintains the consistency and performance of a monolith, while offering the flexibility of a segmented deployment.
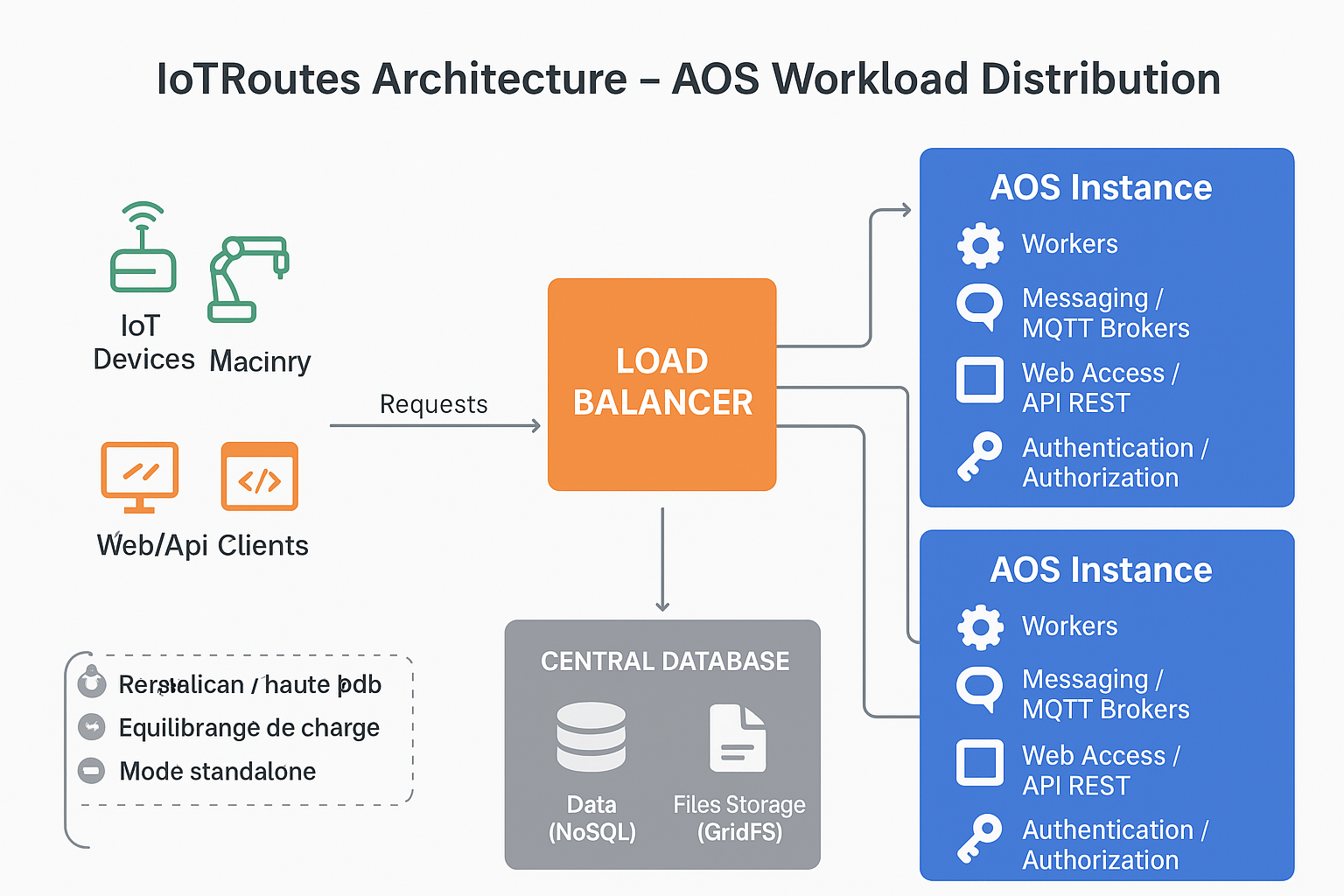
➡ Load distribution
The IoTRoutes backend server, called AOS (Application Object Server), forms the core of the platform.
It integrates all functional modules — including communication, storage, messaging, processing (workers), and the authentication and authorization module.
Distributed Architecture and Redundancy
The AOS is designed to be deployed on one or multiple server instances, depending on performance and infrastructure resilience requirements.
Each instance can host one or more roles (Messaging, Workers, Web Access, etc.), enabling:
Balanced workload distribution across different servers;
Duplication of critical roles (e.g., multiple MQTT brokers or data acquisition workers) to ensure high availability and fault tolerance;
Horizontal scalability, by simply adding new AOS instances assigned to specific roles.
Load Balancing and Performance
In large-scale or production environments, AOS servers can be placed behind a Load Balancer.
The Load Balancer automatically distributes requests and processing tasks among the available instances, optimizing:
Service availability,
Dynamic distribution of user and IoT traffic,
and the overall responsiveness of the platform.
Deployment Modes
Centralized mode (standalone): a single AOS instance hosts all roles — ideal for testing, demonstration, or lightweight deployments.
Distributed mode: multiple AOS servers share or duplicate roles based on load or service criticality, enabling a robust and scalable deployment for larger infrastructures.