Operations
- IoT messages -
The Operations module groups the core day-to-day functionalities of IoTRoutes that users interact with for data analysis, monitoring, and command management.
These functionalities enable users to explore data generated by connected devices, send or monitor commands, and trace workflow executions.
IoT Messages
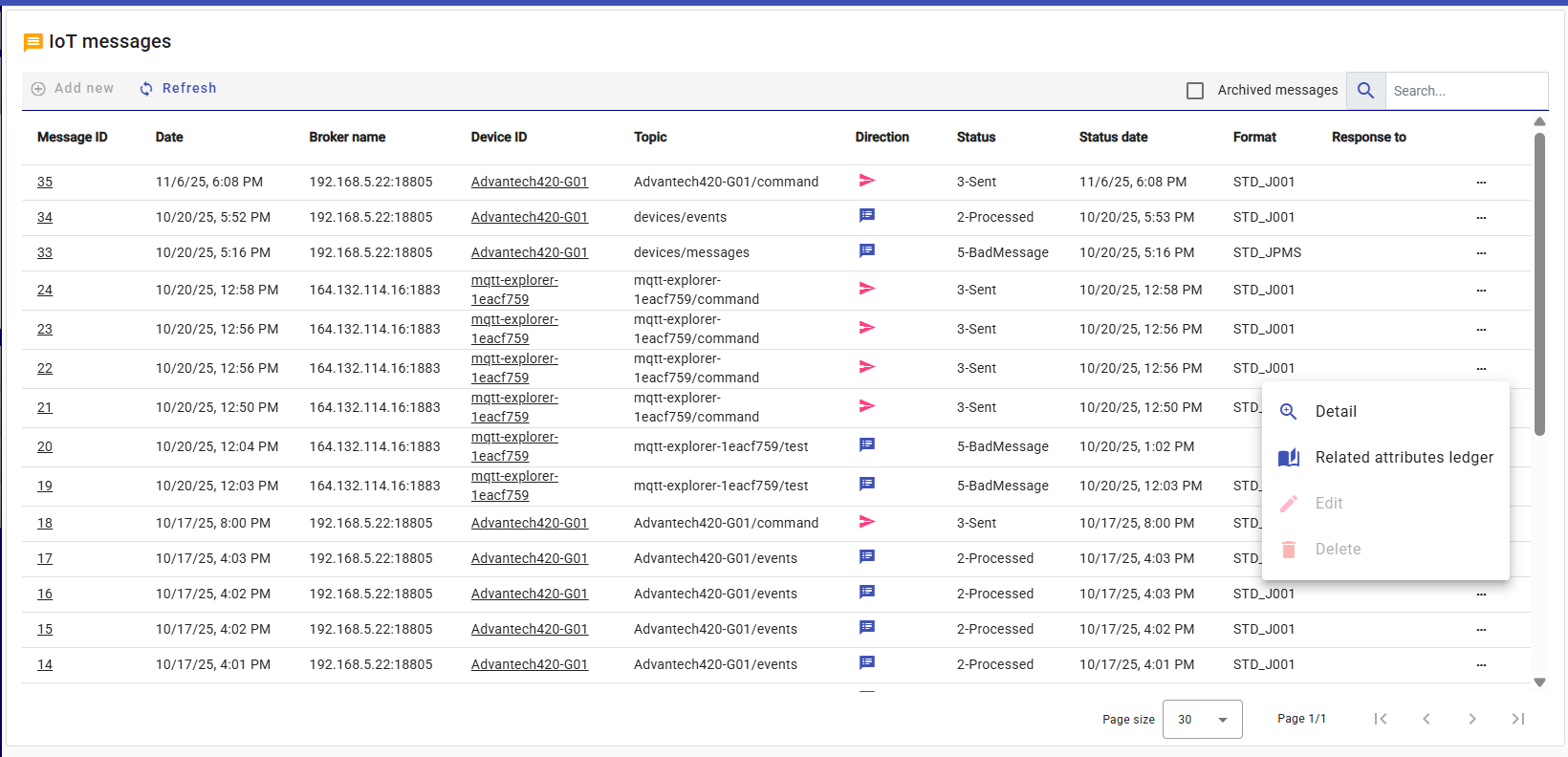
The IoT Messages page displays all device communication records — including both incoming messages and outgoing commands.
Messages are shown along with their status, topic, and direction (inbound or outbound).
Incoming messages are captured from the message broker’s queue and processed by the Inbound Workflow.
This workflow converts each raw message into the Platform Message Structure (PMS), performs schema validation and interpretation, and normalizes the extracted attribute values into the data ledger.
Each workflow can include actions that update the message’s status according to its configured lifecycle (for example: Received → Processed → Archived).
The message list view allows users to:
- Filter and search messages by broker, device, topic, or status
- Open detailed message information by clicking the Details button or the Message ID
- Access related Attribute Ledger entries via the row action buttons, particularly useful for analyzing the normalized data resulting from processed messages.
- Toggle Archived Messages to view historical records.
Archived messages are automatically moved by the Cleaning Workflow, which transfers older or obsolete messages from the active table to an archive table to improve system performance.
This workflow is fully customizable — it can be activated, scheduled, and adjusted to meet your archiving strategy.
By default, it is disabled until explicitly configured.
Message Detail View
When a user clicks a Message ID in the list, the system opens the detailed view of that IoT message.
This page provides full visibility into the message’s metadata and content.
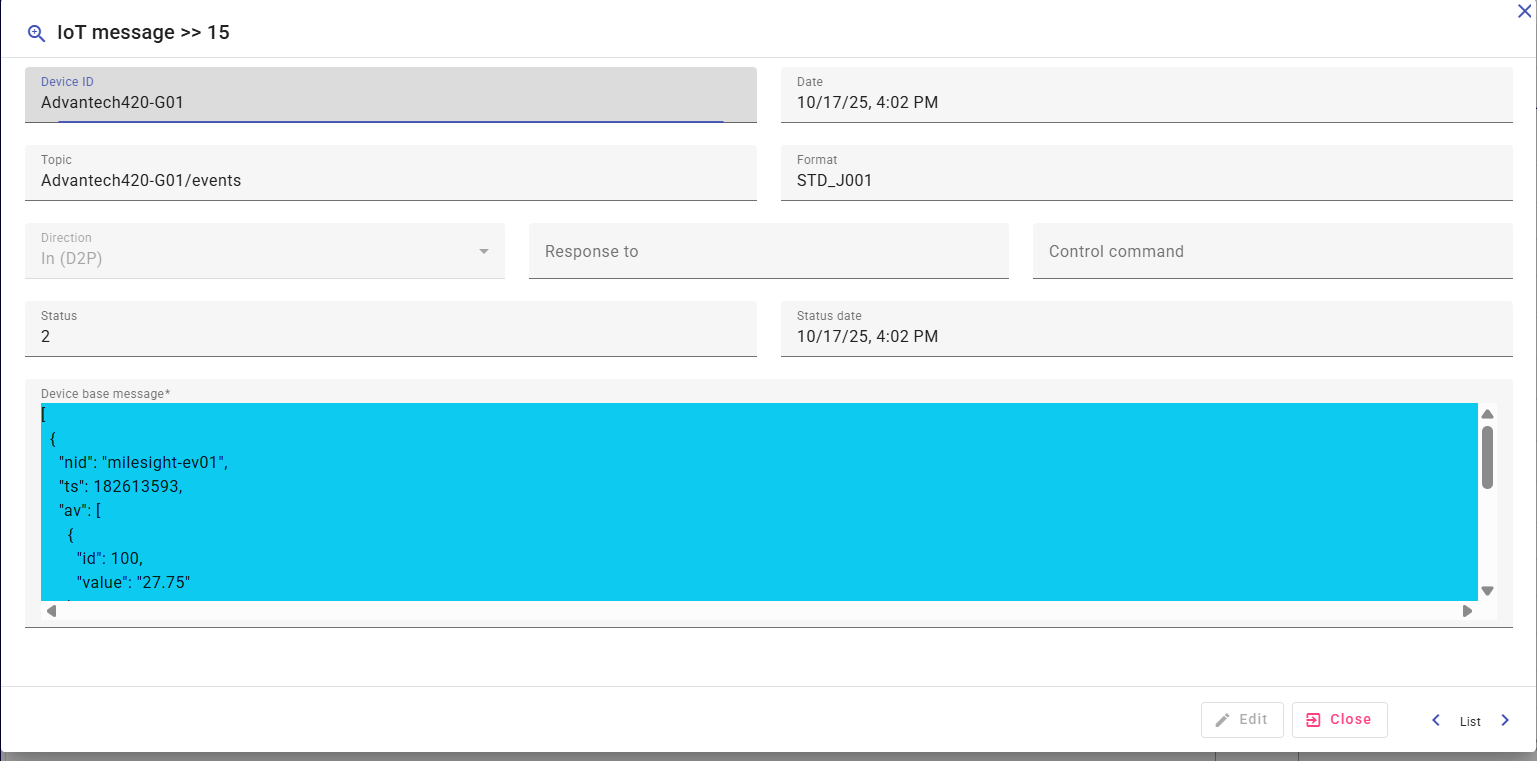
1- Header Information
The upper section summarizes the core metadata for the selected message:
- Device ID – The unique identifier of the device that sent or received the message.
- Date – The exact timestamp when the message was received or sent.
- Topic – The MQTT topic or communication channel used for message transmission.
- Format – Indicates the message format used by device (for example, STD_J001 or STD_JPMS).
- Direction – Specifies whether the message is incoming (D2P) — device to platform — or outgoing (P2D) — platform to device.
- Status – Displays the current processing state (e.g., Received, Processed, BadMessage, Sent).
- Status Date – Shows when the message last changed its state in the processing lifecycle.
- Response To – If applicable, references the command or previous message that triggered this one.
2- Device Base Message
This section shows the raw message payload received from or sent to the device.
It is displayed in structured JSON format for easy readability and debugging.
The base message represents the data exactly as transmitted through the broker — before any transformation, normalization, or workflow actions.
Message Lifecycle and Workflow Interaction
Each IoT message in the system passes through a defined lifecycle that reflects its processing status and the actions performed by various workflows.
This lifecycle ensures full traceability — from the moment a message is received from a device, until it is processed, archived, or triggers downstream logic.
1. Message Reception
When a message is received from a device (via MQTT or another broker), it is inserted into the active message table with:
- Direction: In (D2P)
- Status: 1 - Received
At this stage, the raw payload is still in its native device structure, and has not yet been normalized or interpreted.
2. Inbound Workflow Processing
Inbound workflows automatically process incoming messages to transform them into a Platform Message Structure (PMS).
These workflows typically include:
- Parsing the incoming payload (JSON, binary, etc.)
- Validating the message format
- Mapping device-specific attributes to standardized PMS fields
- Normalizing attribute values and saving them into the ledger
After successful transformation, the workflow updates the message status to:
2 - Processed
If the payload is malformed or fails validation, the message becomes:
5 - BadMessage
3. Outgoing Messages
Messages generated by platform workflows or command tables and sent to devices are registered as:
- Direction: Out (P2D)
- Status: 3 - Sent
Before being sent, the platform builds a PMS JSON payload that can be further adapted by the outgoing workflow to match the target device protocol or structure.
This allows seamless integration with diverse device types.
4. Workflow Actions and Status Changes
Workflows can dynamically update message statuses as part of their configured actions.
For instance:
Marking a message as Acknowledged after a device reply
Flagging as Error if a response timeout occurs
Tagging Archived once retention policies move it out of the active table
Each change is logged with a Status Date timestamp for audit tracking.
5. Archiving and Cleaning
To maintain system performance, older processed messages are periodically archived by dedicated cleaning workflows.
These workflows:
- Move processed records from the active messages table to an archive table
- Are fully customizable (filters, retention periods, frequency)
- Are disabled by default, allowing administrators to activate and configure them as needed
Archived messages remain accessible for consultation through the “Archived Messages” filter in the list view.
